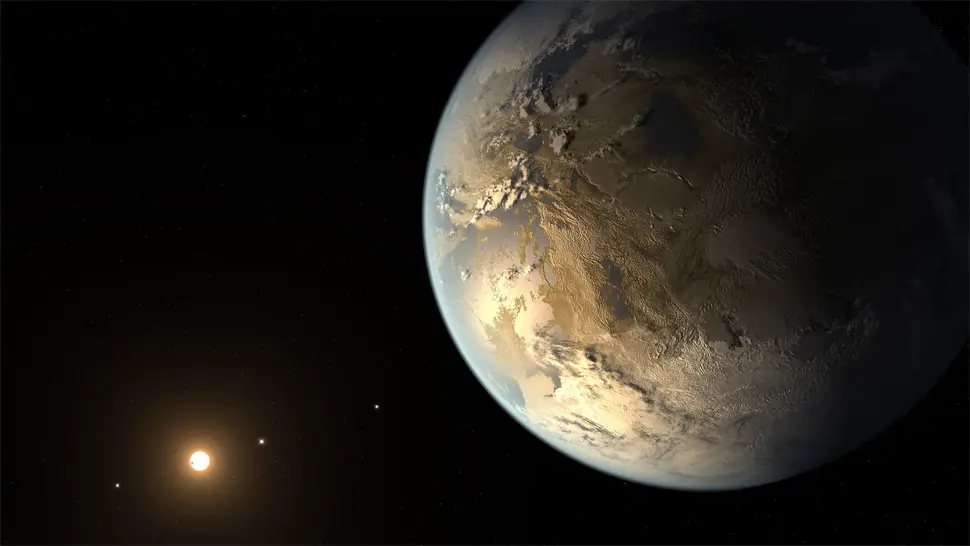
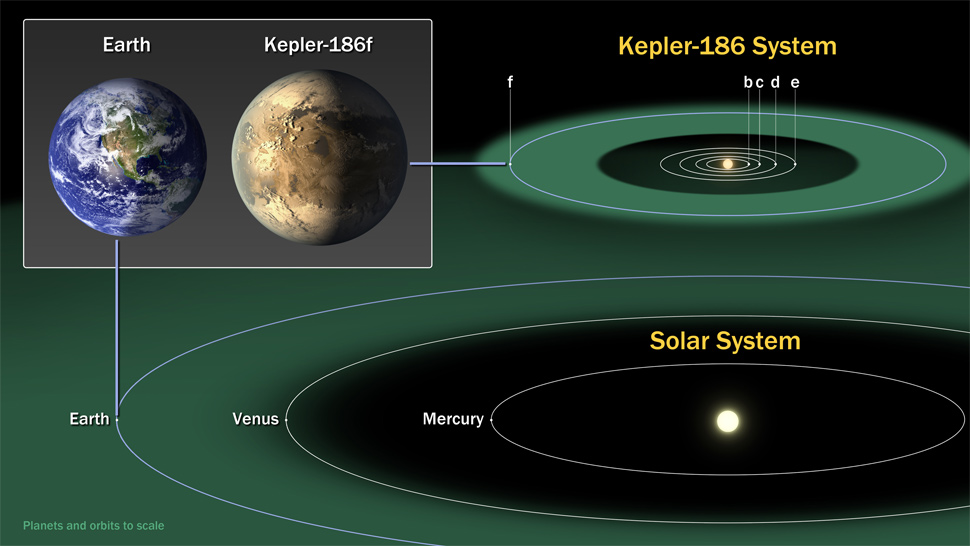
17th April 2014 First Earth-sized exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone of another star has been confirmed NASA has announced the discovery of Kepler 186 f, an Earth-sized exoplanet in the habitable zone of its host star, Kepler 186.
The first Earth-sized exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone of another star has been confirmed by observations with both the W. M. Keck Observatory and the Gemini Observatory. The initial discovery, made by NASA's Kepler Space Telescope, is one of a handful of smaller planets found by Kepler and verified using large ground-based telescopes. It also confirms that Earth-sized planets do exist in the habitable zone of other stars. "What makes this finding particularly compelling is that this Earth-sized planet, one of five orbiting this star, which is cooler than the Sun, resides in a temperate region where water could exist in liquid form," says Elisa Quintana of the SETI Institute and NASA Ames Research Centre, who led the paper published in the current issue of the journal Science. The region in which this planet orbits its star is called the habitable zone, as it is thought that life would most likely form on planets with liquid water. Steve Howell, Kepler's Project Scientist and a co-author on the paper, adds that neither Kepler (nor any telescope) is currently able to directly spot exoplanets of this size and proximity to their host star. "However, what we can do is eliminate essentially all other possibilities, so the validity of these planets is really the only viable option." With such a small host star, the team employed a technique that eliminated the possibility that either a background star or a stellar companion could be mimicking what Kepler detected. To do this, they obtained extremely high spatial resolution observations from the eight-metre Gemini North telescope on Mauna Kea in Hawaii, using a technique called speckle imaging, as well as adaptive optics (AO) observations from the ten-metre Keck II telescope, Gemini's neighbour on Mauna Kea. Together, these data allowed the team to rule out sources close enough to the star's line-of-sight to confound the Kepler evidence, and conclude that Kepler's detected signal has to be from a small planet transiting its host star. "The Keck and Gemini data are two key pieces of this puzzle," says Quintana. "Without these complementary observations, we wouldn't have been able to confirm this Earth-sized planet." The Gemini "speckle" data directly imaged the system, zooming to within about 400 million miles (about 4 AU, approximately equal to the orbit of Jupiter in our Solar System) of the host star and confirming there were no other stellar-sized objects orbiting within this radius from the star. Augmenting this, Keck AO observations probed a larger region around the star but to fainter limits. According to Quintana, "These Earth-sized planets are extremely hard to detect and confirm, and now that we've found one, we want to search for more. Gemini and Keck will no doubt play a large role in these endeavours."
The host star, Kepler-186, is an M1-type dwarf star relatively close to our Solar System at 500 light years and in the constellation of Cygnus. The star is very dim, being over half a million times fainter than the faintest stars we can see with the naked eye. Five small planets have been found orbiting it – four of which are in very short-period orbits and are very hot. The planet designated Kepler-186f, however, is Earth-sized and orbits within the star's habitable zone. The Kepler evidence for this planetary system comes from the detection of planetary transits. These transits can be thought of as tiny eclipses of the host star by a planet (or planets) as seen from the Earth. When such planets block part of the star's light, its total brightness diminishes. Kepler detects that as a variation in the star's total light output and evidence for planets. So far, more than 3,800 candidate planets have been detected by this method with Kepler. The Gemini data utilised the Differential Speckle Survey Instrument (DSSI) on the Gemini North telescope. DSSI is a visiting instrument developed by a team led by Howell who adds, "DSSI on Gemini rocks! With this combination, we can probe down into this star system to a distance of about 4 times that between the Earth and the Sun. It's simply remarkable that we can look inside other solar systems." DSSI works on a principle that utilises multiple short exposures of an object to capture and remove the noise introduced by atmospheric turbulence producing images with extreme detail. Observations with the W.M. Keck Observatory used the Natural Guide Star Adaptive Optics system with the NIRC2 camera on the Keck II telescope. NIRC2 (the Near-Infrared Camera, second generation) works in combination with the Keck II adaptive optics system to obtain very sharp images at near-infrared wavelengths, achieving spatial resolutions comparable to or better than those achieved by the Hubble Space Telescope at optical wavelengths. NIRC2 is probably best known for helping to provide definitive proof of a central massive black hole at the centre of our galaxy. Astronomers also use NIRC2 to map surface features of Solar System bodies, detect planets orbiting other stars, and study detailed morphology of distant galaxies. "Observations from Keck and Gemini, combined with other data and numerical calculations, allowed us to be 99.98% confident that Kepler-186f is real," says Thomas Barclay, Kepler scientist and co-author on the paper. "Kepler started this story, and Gemini and Keck helped close it," he adds.
Comments »
|