11th August 2015 Glacier loss "unprecedented" worldwide A new comprehensive analysis of global glacier changes in the Journal of Glaciology concludes that melting rates are "unprecedented" and occurring faster than ever.
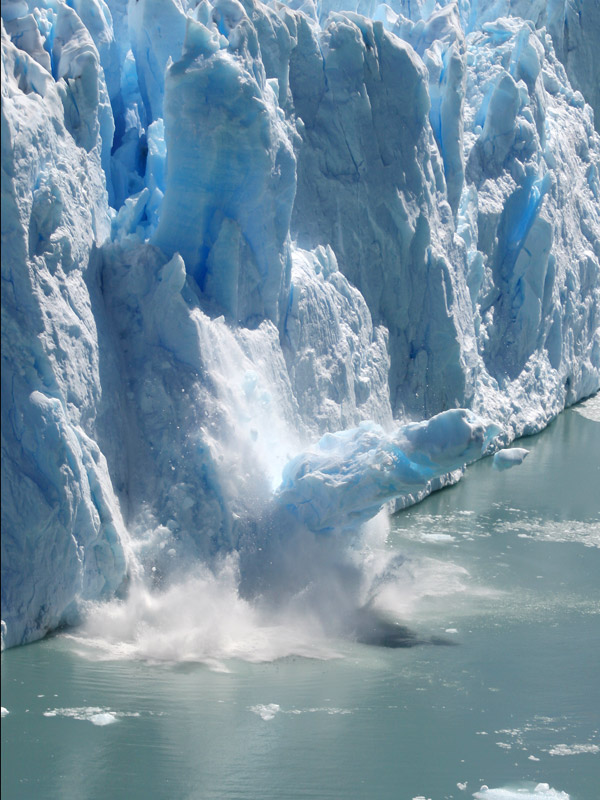
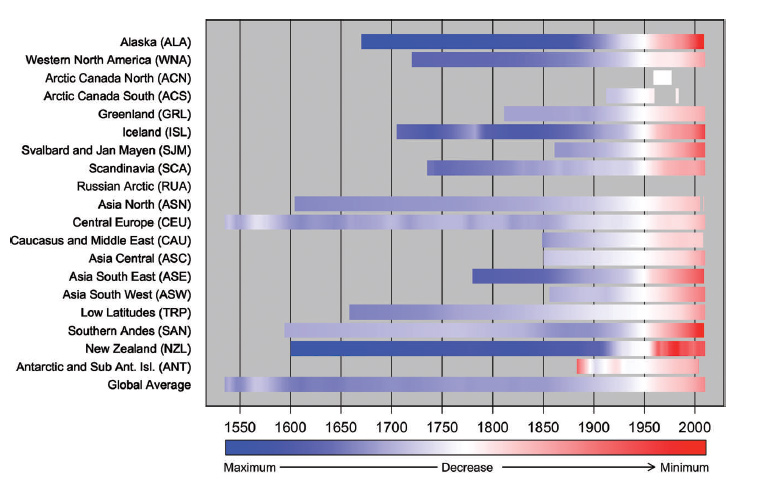
Glacier decline in the first decade of the 21st century has reached a historical record since the onset of direct observations. Glacier melt is a global phenomenon and will continue even without further climate change. That's according to the latest study by the World Glacier Monitoring Service under the lead of the University of Zurich, Switzerland. The World Glacier Monitoring Service, domiciled at the University of Zurich, has compiled worldwide data on glacier changes for more than 120 years. Together with its National Correspondents in more than 30 countries, the international service just published a new comprehensive analysis of global glacier changes in the Journal of Glaciology. In this study, observations of the first decade of the 21st century (2001-2010) were compared to all available earlier data from in-situ, air-borne and satellite-borne observations, as well as reconstructions from pictorial and written sources. "The observed glaciers currently lose between half a metre and one metre of ice thickness every year – this is two to three times more than the corresponding average of the 20th century", explains Michael Zemp, lead author of the study. "Exact measurements of this ice loss are reported from a few hundred glaciers only. However, these results are qualitatively confirmed from field and satellite-based observations for tens of thousands of glaciers around the world."
According to the international author team, the current rate of glacier melt is without precedence at global scale, at least for the time period observed and probably also for recorded history, as indicated also in reconstructions from written and illustrated documents. In addition, the study shows that the long-term retreat of glacier tongues is a global phenomenon. Intermittent re‐advance periods at regional and decadal scales are normally restricted to a subsample of glaciers and have not come close to achieving the Little Ice Age maximum positions reached between the 16th and 19th century. As such, glacier tongues in Norway have retreated by some kilometres from the maximum extents in the 19th century. The intermittent re-advances of the 1990s were restricted to glaciers in the coastal area and to a few hundred metres. In addition, the study indicates that the intense ice loss of the past two decades has resulted in a strong imbalance of glaciers in many regions throughout the world. "These glaciers will suffer further ice loss – even if climate remains stable", warns Michael Zemp. In the coming decades, the loss of glaciers worldwide could have profound implications for many countries that rely on them for water. This is likely to be a particular problem in southeast Asia. For example, another recent study suggests that the glacier volume of the Mount Everest region will fall below 50% of its 2015 level by the middle of this century.
Comments »
|